Why a new benchmark?
Existing retrieval benchmarks primarily consist of text-based queries where keyword or semantic matching is usually sufficient. Many real-world queries contain multimodal elements, particularly images such as diagrams, charts, and screenshots that require intensive reasoning. We introduce MM-BRIGHT to address this gap.
MM-BRIGHT
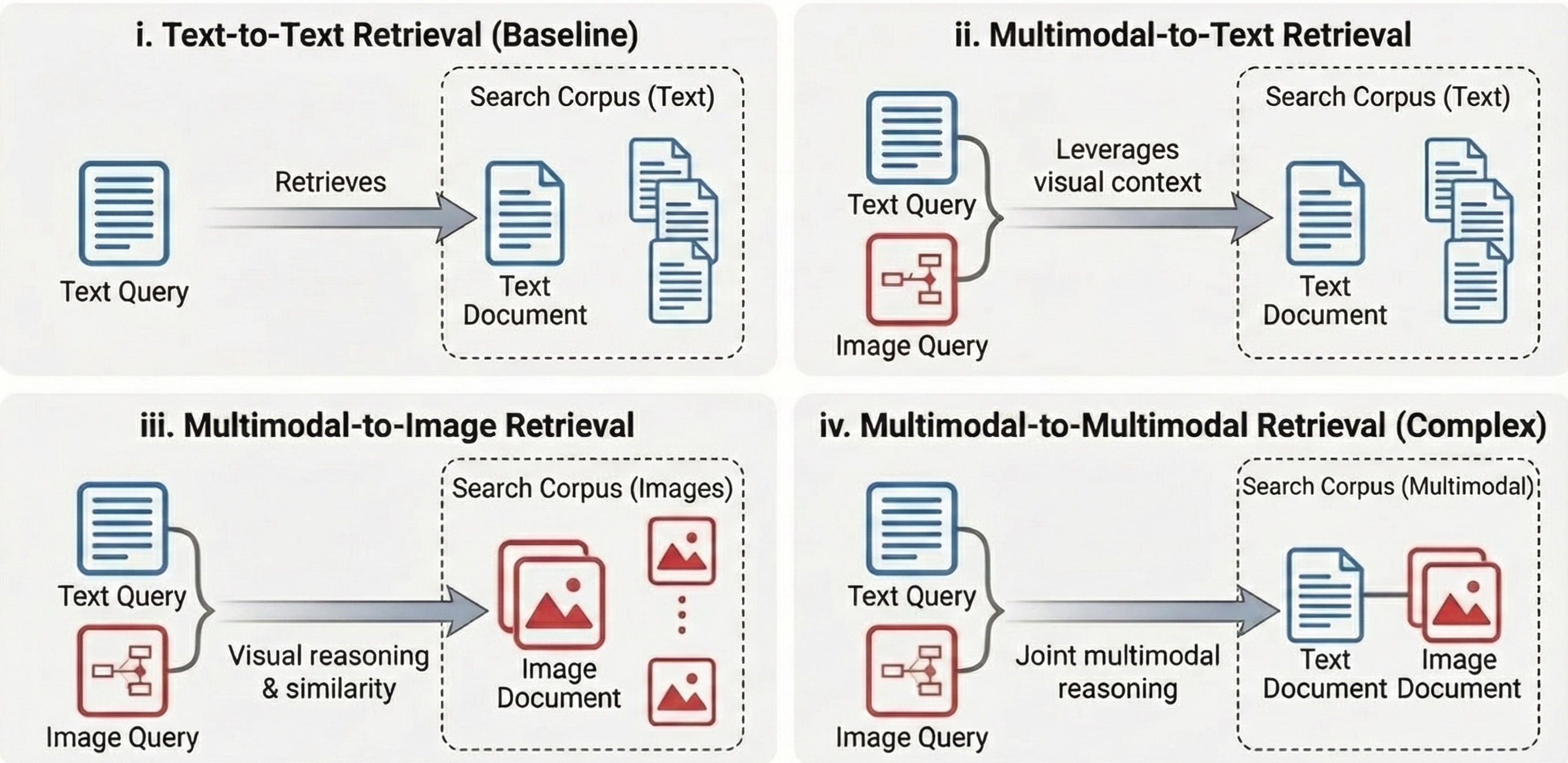
MM-BRIGHT is the first multimodal benchmark for reasoning-intensive retrieval. It consists of 2,803 real-world queries spanning 29 diverse technical domains, with four tasks of increasing complexity: text-to-text, multimodal-to-text, multimodal-to-image, and multimodal-to-multimodal retrieval.
Leaderboard submission
If you would like to submit your results to the leaderboard, please open a pull request or issue on our GitHub repository.
Have Questions?
Contact the authors or open an issue on GitHub.
Leaderboard
Query → Documents: Text-only retrieval showing Avg NDCG@10 across 29 domains.
| Rank | Model | Type | Avg NDCG@10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🥇 1 | DiVeR | Reasoning | 32.2 |
| 🥈 2 | OpenAI | Proprietary | 28.8 |
| 🥉 3 | ReasonIR | Reasoning | 28.6 |
| 4 | Qwen2 | Dense >1B | 28.1 |
| 5 | SFR | Dense >1B | 26.9 |
| 6 | E5 | Dense >1B | 25.3 |
| 7 | GritLM | Dense >1B | 25.3 |
| 8 | Rader | Reasoning | 24.9 |
| 9 | Qwen | Dense >1B | 21.5 |
| 10 | Contriever | Dense < 1B | 20.1 |
| 11 | BM25 | Sparse | 8.5 |